...
- If you find an issue but do not know how to write code for it, please report it on the PrestaShop Forge, our bug-tracking system: read the "How to use the Forge to contribute to PrestaShop" chapter to learn more.
- If you are a software developer, you can help the development of PrestaShop by fixing problems that have been reported by you or another person in the Forge.
- If you want to help fix a bug by writing a patch, there are a few steps to follow. In short, your submission should be made as a pull request on GitHub. See below.
- If you have never used Git or Github, read the instructions at the bottom of the page.
| Info |
|---|
As a contributor, you retain the copyright to your code. However by submitting it to PrestaShop's repository, you are releasing it under either of these licenses:
|
...
This is the recommended way of contributing code to PrestaShop.
In order to make changes to PrestaShop's code, you first need to create a local fork of PrestaShop, or at least have your own Github repository. When your changes are done, you must send your work to the PrestaShop developers for approval. This means installing a tool to retrieve the PrestaShop code from Github, edit it at will on your machine, and send your changes back to PrestaShop's Github repository.
...
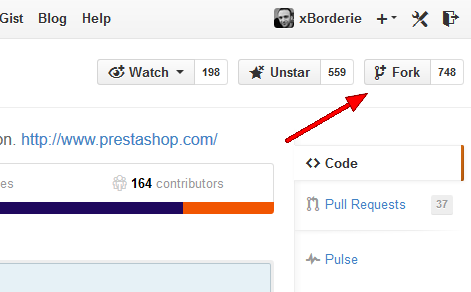
- Go to the PrestaShop Github repository.
- Fork the project by clicking on the "Fork" button. The fork will appear as a "PrestaShop" repository in your own account.
You've successfully forked the PrestaShop repository, but so far it only exists on your Github account. To be able to work on the project, you will need to clone it to your local machine. - On your local machine:
- Clone your fork:
- Create a new folder on your local machine. We'll name it "PS-MyChanges", but you can use whatever name you want.
- Get the HTTPS clone URL from your Github PrestaShop repository. It should resemble this: https://github.com/xBorderie/PrestaShop.git
- Right-click on you your PS-MyChanges folder, and in the Git section of the menu that appears, choose "Git Clone..."
- In the window that opens, paste the clone URL in the "URL" field and the final "\PrestaShop" mention in the "Directory" field, so that the files are downloaded at the root of the folder.
- If you want TortoiseGit to remember your Github username instead of asking it every time you push content to your online repository, you can add that username to your clone URL. For instance, in my case, that's https://[email protected]/xBorderie/PrestaShop.git. Note that TortoiseGit will still ask for your password. You can store that too in the clone URL, but it is not recommended, for obvious reasons: https://xBorderie:[email protected]/xBorderie/PrestaShop.git.
- Click OK: TortoiseGit will download the files and folders from your Gihub Github repo.
- (optional) Add the "upstream" remote: When a repository is cloned, it has a default remote repository called "origin" that points to your fork on GitHubGithub, not the original PrestaShop repository it was forked from. To keep track of the changes in the original repository and keep your local clone updated, you need to add another remote named "upstream":
- Right-click on the PrestaShop folder in the PS-MyChanges folder (it should have a green mark if no change has been made yet), and in the ToroiseGit at the bottom of the TortoiseGit submenu, choose "Settings..."
- Open the Git/Remote section of the option panel.
- Type "upstream" in the "Remote field".
- From PrestaShop's Github repository, copy the HTTPS clone URL and paste it in TortoiseGit's "URL" field. It should https://github.com/PrestaShop/PrestaShop.git.
- Click the "Add new/Save" button. TortoiseGit asks you if you want to disable tag fetching: choose "No".
- TortoiseGit asks you if you want to fetch remote branches from the newly added remote: choose "Yes".
- TortoiseGit displays a summary window: click "OK". A window will open showing that Git is fetching data. Close it once it is done, and close the still-open Settings window.
- Clone your fork:
2. Making your changes and pushing them to your Github repository
Edit all the necessary files that you want to change. As soon as you save and an edited file, Windows will change its the file's icon from green to red to indicate that it has been changed since the last update.
Once you are done editing the local files:
- Reach the root of your local repository (the "PrestaShop" folder in above PS-MyChanges). Right-click on the folder PS-MyChanges and choose "Git Gui". Commit -> 1.6", with "1.6" being your current branch. This will open an interface window. The files you have changed should appear in the "Staged Changes (Will commit)made" section. If they are in the "Unstage Changes" window instead, select them and click on the "Stage Changed" button to move them to the "Staged Changes" section.
- Make sure to only stage the files that you meant to change for this commit, but not any other changed files! For instance, PrestaShop and its modules might change some configuration files: do not ever stage then commit them!
If there are files that you did not change yourself or do not want to commit at this time, simply deselect them before clicking "OK".
- Make sure to only stage the files that you meant to change for this commit, but not any other changed files! For instance, PrestaShop and its modules might change some configuration files: do not ever stage then commit them!
- Write a commit message for your changes. Be sure to follow the commit message norm.
- Click the "CommitOK" button: your changes are now committed to your local Git repository. Click the "Push" buttonClick "Close".
- Right-click on the PS-MyChanges and choose "Git Sync...": a window opens, asking you to which branch the local commit should be pushed – usually it should be "1.6". Leave "origin" as the remote settingURL, and click "Push".
- TortoiseGit open a updates the window showing with the current status, and might also open an OpenSSH window asking you for your Github username, then your Github password. Give them both and validate: the status window should push your changes to your Github repository (see above).
- Success! You can close the TortoiseGit windows: the rest will happen on Github.
...
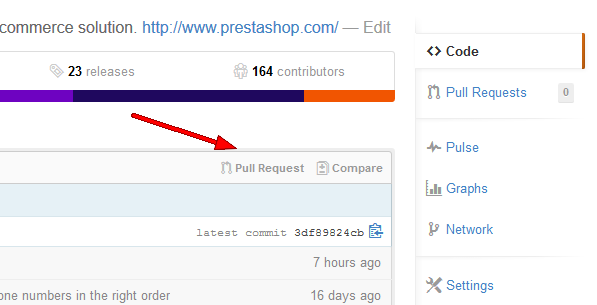
- Go to your own PrestaShop repository on Github.
- Either click on the "Pull Request" or the "Compare" button. Both will open the same screen, comparing your latest commit to the original code.
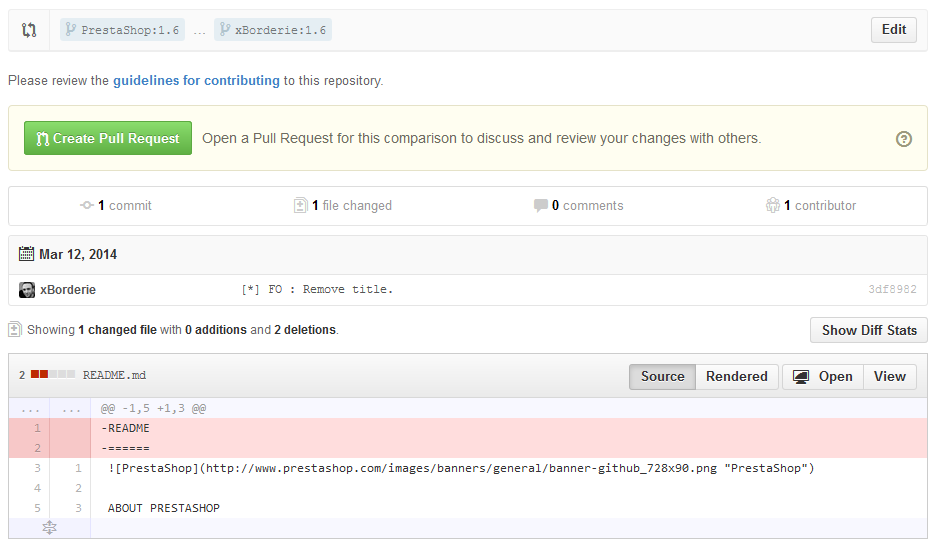
- The top of the screen indicates what is being compared. It should be PrestaShop's 1.6 branch with your own 1.6 branch. You should not have anything to change here, just make sure that the base fork is the PrestaShop repository, and that your own repository is the head fork.
- Click on the "Create a pull request" button. A new screen should appear, in which you can review your changes and give your pull request a title (it should already use the commit message you used from your local clone).
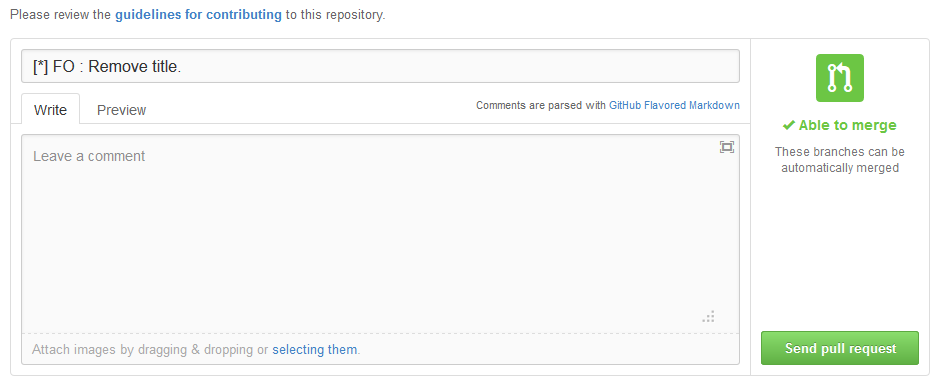
- This title is only for internal use at Github: it helps the developer, but only your commit message is kept in the project's Git history. In any case, most of the time you won't need to it the title: keep the commit message.
- Click on the "Send pull request" button: Github open a screen where you can start a conversation about your pull request, right in PrestaShop's Github repository.
- Congratulation, your changes are now ready to add to the PrestaShop codebase!
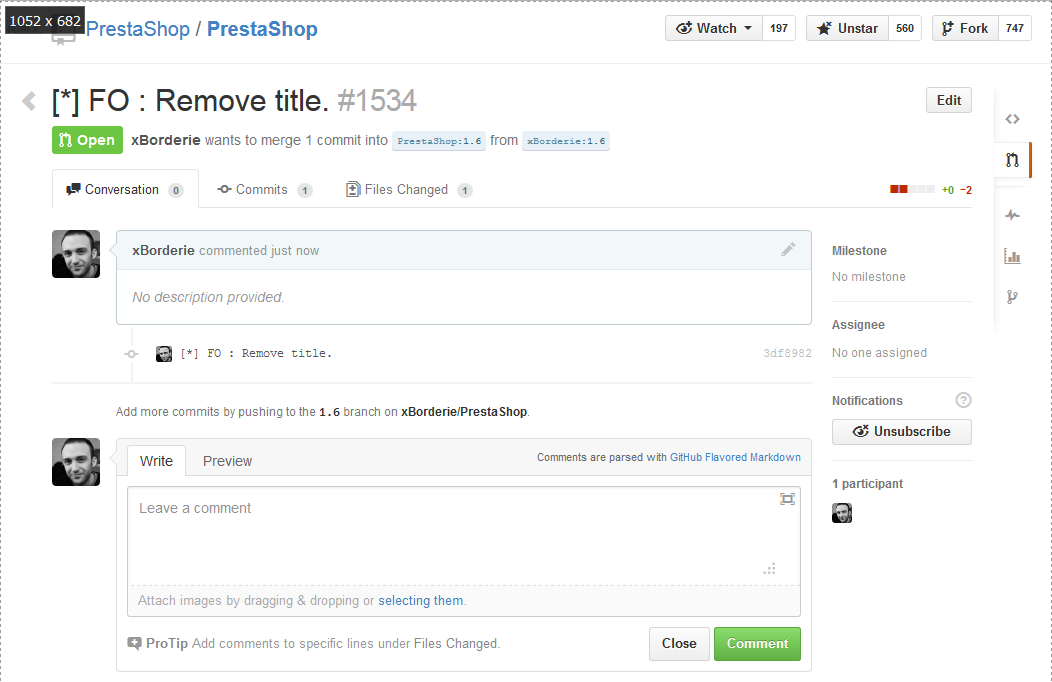
Wait for one of the core developers either to include your change in the codebase, or to comment on possible improvements you should make to your code. Once your pull request is accepted, you will receive an e-mail, and the discussion section will look like this:
Keeping your fork and clone up to date
...
- Right-click on the PrestaShop folder in the PS-MyChanges folder, and in the ToroiseGit TortoiseGit submenu, choose "Settings..."
- Open the Git/Remote section of the option panel.
- Type "upstream" in the "Remote field".
- From PrestaShop Github repository, copy the HTTPS clone URL and paste it in TortoiseGit's "URL" field.
- Click the "Add new/Save" button. TortoiseGit asks you if you want to disable tag fetching: choose "No".
- TortoiseGit asks you if you want to fetch remote branches from the newly added remote: choose "Yes".
- TortoiseGit displays a summary window: click "OK". A window will open showing that Git is fetching data. Close it once it is done, and close the still-open Settings window.
...
- On your local machine:
- Always pull the latest changes from the upstream repository. This will prevent bad surprises, where you cannot push your changes until you have merged the ones that were made by other developers!
- Make your changes:
- Edit all the necessary files. As soon as you save and edited file, Windows will change its icon from green to red to indicate that it has been changed since the last update.
- Submit your changes to your Github repository:
- Once you are done editing the local files, reach the root of your local repository (the "PrestaShop" folder in above PS-MyChanges).
- Right-click on the folder PS-MyChanges and choose "Git Gui". Commit -> 1.6", with "1.6" being your current branch. This will open an interface window. The files you have changed should appear in the "Staged Changes (Will commit)made" section. If they are in the "Unstage Changes" window instead, select them and click on the "Stage Changed" button to move them to the "Staged Changes" section.
- Write a commit message for your changes. Be sure to follow the commit message norm.
- Click the "CommitOK" button: your changes are now committed to your local Git repository. Click the "Push" buttonClick "Close".
- Right-click on the PS-MyChanges and choose "Git Sync...": a window opens, asking you to which branch the local commit should be pushed – usually it should be "1.6". Leave "origin" as the remote settingURL, and click "Push".
- TortoiseGit open a updates the window showing with the current status, and might also open an OpenSSH window asking you for your Github username, then your Github password. Give them both and validate: the status window should push your changes to your Github repository (see above).
- Success! You can close the TortoiseGit windows: the rest will happen on Github.
- Submit your changes to the PrestaShop repository:
- Go to your own PrestaShop repository on Github.
- Either click on the "Pull Request" or the "Compare" button. Both will open the same screen, comparing your latest commit to the original code.
- The top of the screen indicates what is being compared. It should be PrestaShop's 1.6 branch with your own 1.6 branch. You should not have anything to change here, just make sure that the base fork is the PrestaShop repository, and that your own repository is the head fork.
- Click on the "Create a pull request" button. A new screen should appear, in which you can review your changes and edit your commit message (it should already use the commit message you used from your local clone).
- Click on the "Send pull request" button: Github open a screen where you can start a conversation about your pull request, right in PrestaShop's Github repository. Congratulation, your changes are now ready to add to the PrestaShop codebase!
- Wait for one of the core developers either to include your change in the codebase, or to comment on possible improvements you should make to your code.
...
This is not the recommended way to contribute code, and should only be seen as alternative if you don't feel comfortable forking the project or using Git altogether. One of the issues of this method is that it might bring hundreds of untested pull requests to the PrestaShop developers, who are already trying hard to focus on their own assigned projects...
...