System Administrator Guide
Before you begin, you must first install PrestaShop.
This guide will help you configure a walled Web server.
PHP configuration
Basic configuration
To configure PHP, you must edit the php.ini file.
The register_globals rule, when activated, defines all environment variables (GET, POST, COOKIE, SERVER...) as global variables. It is unsafe to use unset variables, because a user could easily set a value into this variable by using the GET method, for example. It is therefore imperative to set register_globals to OFF.
The magic_quotes directive automatically adds slashes to all characters (', ", \, NULL) for all types (GET, POST, COOKIE). This option must be set to OFF because it will addslash each variable even if it does not need to be addslashed. Moreover, some Web applications overlook this option, so some variables will be addslashed twice.
The allow_include_url rule is used to allow to include any file via the require and include statements, even if it is not come from your Web server. This option must be set to OFF, because if one application on your web server suffers of include vulnerability, users will be able to include any file from any server and those will be executed on your own server.
Safe Mode configuration
PHP Safe Mode enables you to limit access to some potentially harmful functionalities, and forbid others. It is useful to establish a security perimeter, by configuring a Web folder as base folder and forbidding PHP to come down this one.
To activate Safe Mode, you just need to set “safe_mode” to “On” into php.ini file. This is a configuration example:
safe_mode = On safe_mode_gid = Off ; ... safe_mode_include_dir = ; ... safe_mode_exec_dir = “/var/www/bin” safe_mode_allowed_env_vars = PHP_ safe_mode_protected_env_vars = LD_LIBRARY_PATH,LD_PRELOAD ; ... open_basedir = “/var/www/prestashop” disable_functions = shell_exec,system,sleep,syslog,link,sockopen,ftp_connect, pfsockopen,socket_connect,usleep,symlink,virtual,ini_set,ini_alter, ini_restore,passthru,popen,exec disable_classes = ; ... register_globals = Off magic_quotes_gpc = Off allow_url_fopen = Off allow_url_include = Off ; ... [MySQL] mysql.allow_persistent = On mysql.max_persistent = -1 mysql.max_links = -1 mysql.connect_timeout = 10 mysql.trace_mode = Off ; ... [Session] session.save_handler = files session.save_path = “/var/www/sessions” session.use_cookies = 1 session.name = PHPSESSID session.cookie_path = / session.cookie_domain = session.cookie_httponly = session.serialize_handler = php
- Safe Mode:
- safe_mode_gid: Turned on, PHP will just verify group’s file and not owner.
- safe_mode_include_dir: All files into the directory given, will not be checked by PHP.
- safe_mode_exec_dir: Put here the folder containing binaries application allowed to execution by using exec() function for example.
- safe_mode_allowed_env_vars: PHP will allowed to only modified environment variables which prefix appears here.
- safe_mode_protected_env_vars: This rule permit to forbid modification of variables which prefix appears here.
- open_base_dir: Put here the base application folder. Your web applications may not come down of this folder.
- disable_functions: Put here every functions you want to disable. If you try to call one of these, an exception will be called.
- disable_classes: Put here each classes you want to disable.
- For more information about Safe Mode rules: http://fr.php.net/manual/en/features.safe-mode.php
- MySQL:
- mysql.allow_persistent: Turn on if you want to enable mysql to have persistent connection (mysql will close its connections after several HTTP request)
- mysql.max_persistent: Put here the maximum number of persistent connections allowed by MySQL (-1 correspond to the maximum that system can offer)
- mysql.max_links: Put here the maximum number of connections allowed by MySQL (-1 correspond to the maximum that system can offer)
- mysql.connec_timeout: Put here the number of seconds MySQL must wait before declare connection as lost.
- mysql.trace_mode: When this mode is activated, MySQL will show errors when there is non-free ressources or a MySQL error.
- For more informations about MySQL directives:
- http://fr.php.net/manual/en/mysql.configuration.php
- Session:
- session.save_handler: Define the name of session’s handler. It will be used to save and read data.
- session.save_path: Put here the directory where session will be saved.
- session.use_cookie: Notice if server will use cookie to save customer’s sessions.
- session.name: Notice the name of session, which is used as cookie name.
- session.cookie_path: Specialize the path used during cookie creation.
- session.cookie_domain: Specialize the domain used during cookie creation (default: “/”). If it is empty, server’s host name will be used according to the cookie’s specifications.
- session.cookie_httponly: Turned on, cookie will only be available by HTTP protocol. It means cookie will not be available by script language, like Javascript. This configuration allows to limit XSS (but it is not supported by every web browser).
- session.serialize_handler: Defines the name of the handler which is used to serialize/deserialize data.
- For more informations about session: http://fr.php.net/manual/en/session.configuration.php
The only problem is Safe Mode is included in PHP. If PHP machine is vulnerable then user could bypass this Safe Mode. If you have several web applications on the same server, or if you just want to protect your server by an other solution, I invite you to read the first paragraph of the recommendations part.
MySQL configuration
MySQL have an administrator account as default, which permit access to all data-base’s data, no matter the database. The administrator have all rights and can do every possible actions. To prevent an application A to be vulnerable when one of your server application have a SQL injection (if user succeed in recover the administrator password), you need to walled your databases.
For each new web applications installed, you need to create a new MySQL user who just have necessary rights.
We just installed prestashop. We have a MySQL user with rights to create new users:
mysql -u user -p password mysql: mysql> USE mysql; mysql> CREATE USER 'new_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'new_password';
For now, we created a user ‘new_user’ who just have rights to local connect and have ‘new_password’ as password.
We now allow this user to use the ‘prestashop’ database and, at the same time, configure his rights:
mysql> GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE, DROP
> ON `prestashop`.* TO 'new_user'@'localhost';
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
We have now one user just for our ‘prestashop’ database. Think to do this for each new web application you add.
If you just installed MySQL, think to add a password for the root account, who has no password as default.
Basic authentication establishment (htaccess)
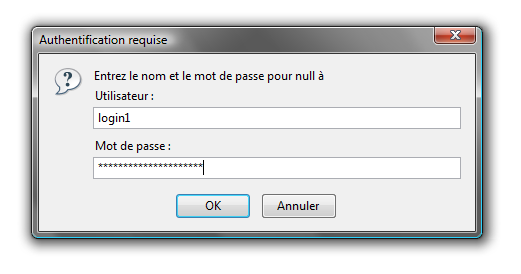
Now, we are going to established a basic authentification on the prestashop’s admin directory.
Principe of htaccess is to protect, by using an self-supported authentification, a directory and all its sub-folder by adding a .htaccess file in this directory.
So, we add a .htaccess file in the prestashop admin folder (/var/www/prestashop/admin):
AuthUserFile /var/www/.prestashop_admin AuthName "Prestashop Admin Access" AuthType Basic Require valid-user Options -Indexes
Explanation:
- AuthUserFile: Shows the path to the file containing allowed users and their passwords.
- AuthName: Defines the message to show when the authentication window pop.
- AuthType: Defines the authentication type.
- Require valid-user: Shows that we need to be authenticated to read this folder.
- Options: Defines folder’s options. Here ‘-Indexes” fobids directory browsing on this folder.
Here the content of .prestashop_admin file:
login1:$apr1$/wJeliK8$e9OzgRaVL8J8wSsFBXjor1 login2:$apr1$yV65Kqqz$cFt3sV2.Q7hhLRRUJDo5a/
This file contains logins and hashed password who are allowed to access to the folder.
To hash password, you can follow this link: htpasswd file generation.
It is strongly recommend to put this file into an inaccessible directory by your wep applications and so before the “openbase_dir” folder. It prevent of htpasswd file injection if one of yours web applications is vulnerable.
Example:
It is also possible to perform IP and domain restrictions:
Order Allow, Deny Deny from all Allow from .myboutique.com Allow from 127.0.0.1
However, it is strongly inadvisable to put this kind of directives:
<LIMIT GET POST> Require valid-user </LIMIT>
Recommendations
suPHP Installation
As we said before, PHP Safe Mode is a part of PHP machine and if PHP machine is vulnerable (it’s append), user can potentially bypass this Safe Mode. There is a solution: suPHP.
suPHP is an Apache module which allowed to control and walled web applications, in order that even if user bypass Safe Mode, it will be control and stop by an other protection: suPHP.
You find documentation and download here: suPHP.
Updates
Sometimes it is not PHP developer code which is vulnerable, so it is strongly recommended to update server’s application (PHP, MYSQL, Apache) and the rest.
There is a command on UNIX/BSD system: cron, which allowed to execute programmed actions based on configuration files (edited with crontab). It permit to automate application’s update, and to backup files and databases without an administrator intervention.
It just limit the authentication to GET and POST HTTP Request, but it is possible to bypass this and get the content of a known page.